It is an overwhelming hit among the roofs and it symbolizes the eco-friendly dream but how to hack it? Building a green roof is not exactly a piece of cake but the outcome is definitely worth it. In this article, you will find a general introduction and explanation of the layers that the green roof consists of. It should be enough for you to consider its pros and cons, let’s see!
The green roof is one of the technologically most demanding roofing types. In the vast majority of cases, its environmental benefits are mere advertising tricks and have not much in common with environmental protection or sustainable lifestyle. The internal parts of the structure must be duly protected by a composite layer of hydro insulation and layers preventing the root system from invading the roof structure. The plants on the roof or walls of a building may create a sort of a wrap that cools it down in the hot months.
Which plants to use for the green roof?
Sedum is a group of plants very close to succulents. They are xerophytes, with thick water-storing leaves. Sedum is suitable for roofs where a thick layer of soil cannot be provided to hold enough water all year round.
Green roofs and façades are most easily achieved through suitable kinds of climbers. The most frequent kinds are the ivy, grapevine, or wisteria for example.
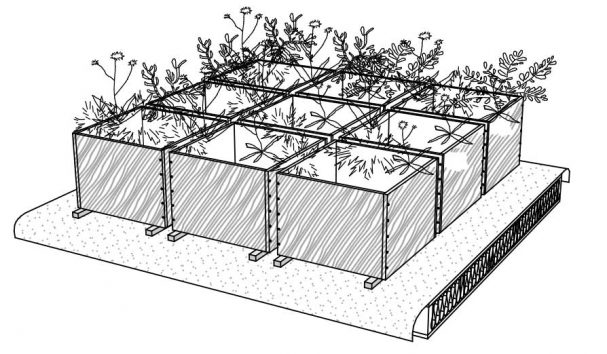
The roof can be planted with plant pots, thus achieving a green effect. There must be a permeable gap between the plant pots and hydro insulation to drain water from the roof surface.
The installation of a simple green roof layer system
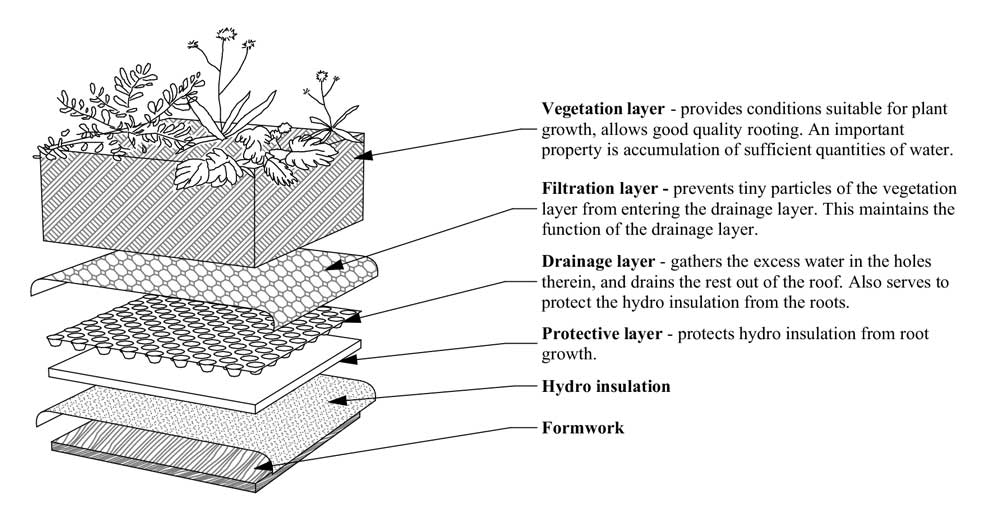
Vegetation layer – provides conditions suitable for plant growth, allows good quality roots. An important property is an accumulation of sufficient quantities of water.
Filtration layer – prevents tiny particles of the vegetation layer from entering the drainage layer. This maintains the function of the drainage layer.
Drainage layer – gathers the excess water in the holes therein, and drains the rest out of the roof. Also serves to protect the hydro insulation from the roots so it does not get penetrated by them
Protective layer – protects hydro insulation from root growth.
Hydro insulation
Formwork
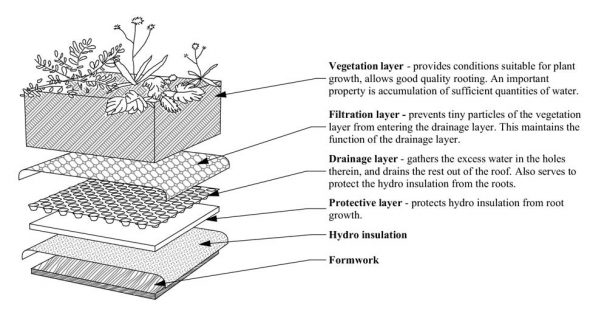
The Simple Green Roof Layer System
– Herbs/grasses/other plants
– Soil substrate
– Grid preventing substrate sliding
– Drainage – catches water
– Hydro insulation by bitumen sheets
– Roof formwork (OSB/particle board)
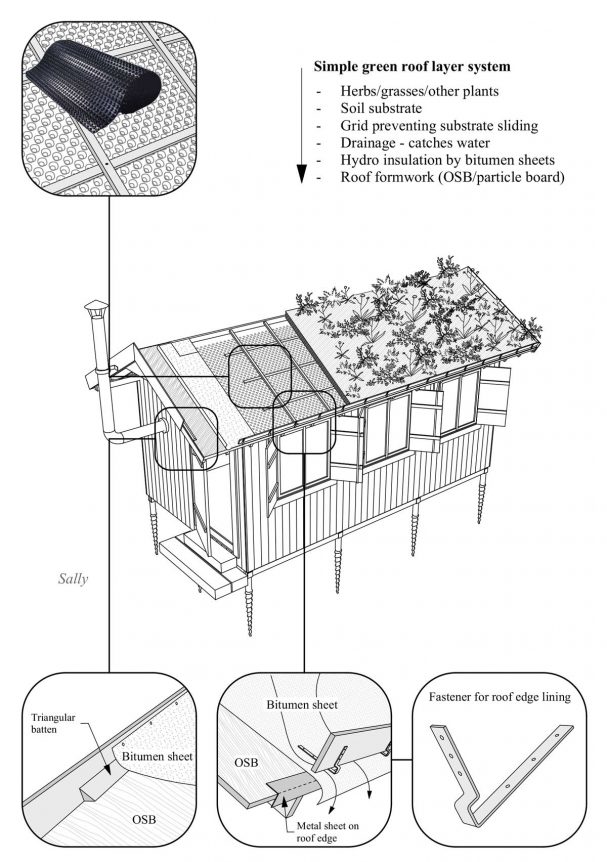
Overall, the green roof construction has certain fixed rules that cannot be avoided but besides that, it can be very creative, enjoyable and most rewarding once it sits on your tiny house. Have a look at the plans we have designed and see for yourself to which one would the green roof suit the most. Lola, the eco-friendly small house would seem like a perfect fit.
If you have decided to go the most sustainable way possible, there is also a very popular article about How to plan for a more eco-friendly home on our blog.
Have fun!









