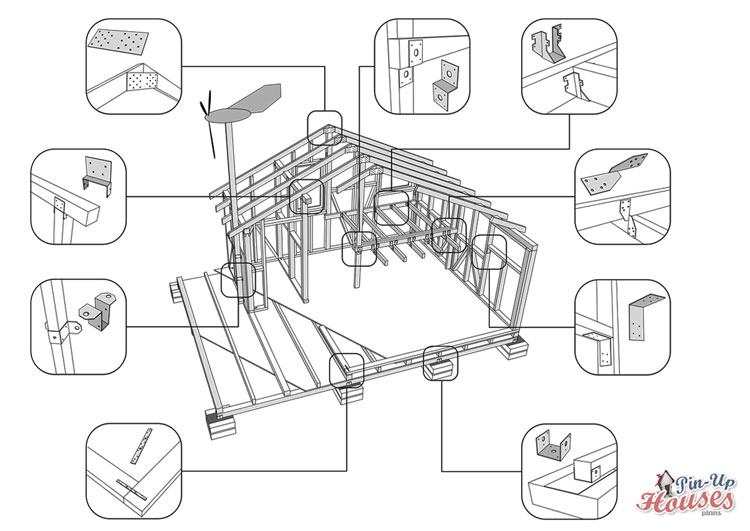
Small house timber connectors

A highly important item when it comes to DIY house plans construction are the small house framing connectors: components that attach different elements of the house to each other. They need to be effective in order to provide a proper structural support and stability and their strength and stiffness become crucial during extreme events such as for example bad weather conditions.
Therefore choosing a proper fastening material and woodworking joints – meaning nails, bolts, various woodworking fasteners, hinges etc. – is very important. It is recommended to buy this equipment in one of the big hardware stores and in case of the woodscrews, you can definitely buy whole boxes as they are crucial to the construction. It is more cost effective and also any left overs will definitely be needed sooner or later in your wooden tiny house. When categorizing the connections, we distinguish two main divisions: mechanical framing connectors and traditional woodworking joints known also as carpentry joints.
Mechanical framing connectors
Dowel-type mechanical metal fasteners
Probably the most typical in timber structure and among mechanical metal fasteners are dowel-type mechanical connectors, primarily joints, nails, screws, bolts or timber rivets. Their advantages lie in effectivity when it comes to transferring loads while still being simple and not requiring a complicated installation. Nails are probably most common in small timber structures with light loads, as well as screws, which have the advantage of smaller tendency to go loose and better resistance to wind or moisture exposure.
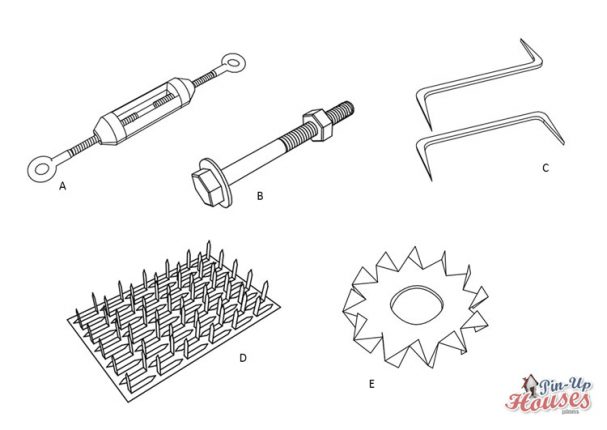
- A. Tension rod system
- B. Bolts
- C. Iron cramps
- D. Gusset plate
- E. Double sided toothed timber connector plate
Similarly looking to screws are bolts. They have also threaded shank, but keep same diameter throughout its entire length – it is not tempered and does not have a pointed end. Also they come with external nut, which ties from the other side of the two connecting members then the bolt is inserted from. In big timber constructions with high load transfer capacity, timber rivets are useful. They are very ductile high-strength steel fasteners, usually galvanized, with shank flattened into a rectangular cross section and a head, which wedges firmly into holes in pre-drilled metal steel plate, through which timber rivets are driven into the wood without need of pre-drilling. It is crucial to keep them in a position whereby their long axis is parallel to the wood grain in order for them to function properly.
Timber connectors types of nails
There are also several types of nails varying in steel quality, size, surface, cross section dimensions and different factors. Joist nail is a special type, which can be used for stressed joists such as ceiling, profiles, cantilevers, etc. Roofing nail has a narrow shank and a broad head and is often used on bituminous roofing or foils inside wall compositions. Common nail is longer and has smooth surface and a head, commonly used in wooden house construction. Concrete nail has same length, but is thicker and made of good quality steel, which can penetrate concrete. Very similar is a box nail, only its shank is narrower and longer, while the head smaller. Again same length has a casing nail, which is thin with a narrow head and suitable primarily for flooring installations. Longest among the common types of nails is sinkers nail with concrete or vinyl surface finish to facilitate easier penetration and with an anti-slide pattern on the head.
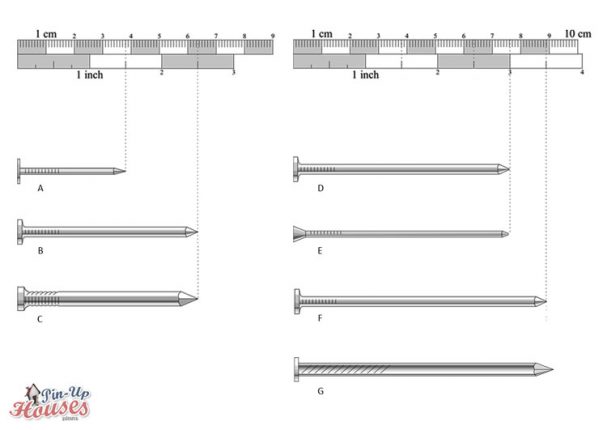
- A. Joist hanger nail
- B. Roofings nail
- C. Common / box / sinkers nail
- D. Concrete nail
- E. Common / box / sinkers nail
- F. Casing nail
- G. Common / box / sinkers nail
Timber connectors types of screws
Among small house framing connectors there are various types of screws, differing in shape and size of shank, suitability for different materials, strength or kind of heads. Traditional wood screws have a tapered shank, which is usually not threaded all the way. They are used primarily for wood and a pilot hole is recommended when screwing them in; then they can fit tightly. An untampered version is also available and means smaller risk of splitting the wood. Drywall screws have shank threaded along all its length coated with black phosphate and are used for connecting drywall to wood or metal studs. Their section is more curved to prevent the dry wall to be torn. MDF screws have a sharp point and double thread at the bottom part to ease the initial penetration of material and hold tightly once they are screwed in. Lag screws are the toughest and sturdiest, used for connecting heavy material and carry heavy loads. They are bigger in size, come only with hex type of head and require predrilling when being installed. Sheet metal screws are threaded all the way. They usually shorter with pan or round type of head and used with sheet material and metal, although they can be used for wood as well.
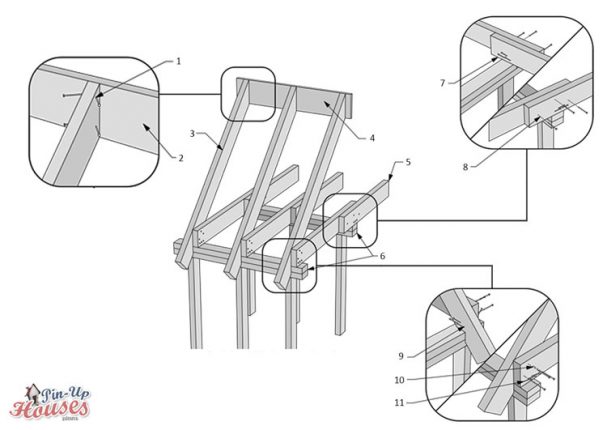
- Two 3,5″ (90 mm) or three 3″ (80 mm) nails, toenail or face nail
- Ridge board
- Roof rafter
- Ridge board
- Ceiling joists
- Double plates
- Ceiling joists to double plate, three 3,5″ (90 mm) or 3″ (80 mm) or 2,5″ (65 mm) nails
- Connecting ceiling joists, three 3,5″ (90 mm) nails or four 3″ (80 mm) nails
- Toenail from rafter into double plate, three 3,5″ (90 mm) or 3″ (80 mm) or 2,5″ (65 mm) nails
- Joining ceiling joists and rafters, three 3,5″ (90 mm) or 3″ (80 mm) or 2,5″ (65 mm) nails
- Toenail from ceiling joists into double plate, three 3,5″ (90 mm) or 3″ (80 mm) or 2,5″ (65 mm) nails
Mechanical fasteners gusset plates
Gusset plates are square or rectangular metal connector plates with integral multiple rows of teeth. They are made of steel, cold-rolled or galvanized, which better for outdoor use due to its better resistance to rust. The steel plates are thick and commonly used for connection of grinders and beams to columns or truss construction to each other, usually in big construction buildings or bridges rather than as small house framing connectors. They partly penetrate the timber structural members, are fastened to them with bolts, rivets or welding and help to increase the overall strength of the joint. It is possible to see gusset plates made of copper or aluminum but much less often and only for small structures requiring less support. Gusset plates can be made into various shapes and painted to visually match its surroundings.
Shear small house framing connectors
Shear connectors are also not that relevant to the DIY house plans, as they are common for heavy bearing loads, fabricated with special machinery tools and their installation require very precise work. They are load transferring connectors made of light metals or cast iron, which hold together two timber members or a timber member with metal side plate and have bolt or lag screws installed in the middle to hold the entire joint together. As they enlarge the area in the wood over which a load is distributed, which makes them more efficient than when the mechanical fasteners are used alone. There are three types, split ring, sheet plates and toothed plates and they are used mostly in roof trusses and other heavy timber or glulam members.
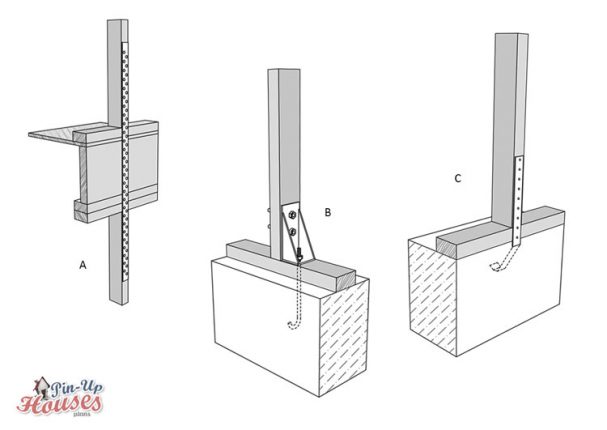
- A. Steel wall-to-wall strap
- B. Steel anchor, hold down either direction
- C. Steel anchor, hold down in concrete
The splits in the split rings allow the connector to slightly deform under load and open or closed in case the wood member changes its volume while still maintaining the contact, while the wedge shapes on sides enable a tight fitting joint and easy installation. Similarly with shear plates, the wood is recessed in order for them to fit flush with the surface. Toothed plates, which can be either single or double sided, have tooth all around their edge penetrating the wood, creating thus again a firm and steady connection.

DIY house plans carpentry joints
Stressed joints use carpentry joints instead of just mechanical metal fasteners in your DIY tiny house to achieve a necessary structural rigidity. Notches, tongues or holes are made in connecting structural members using sharp chisels, drawknives and other tools creating perfectly smooth surfaces in order for the members to perfectly interlock without any gaps or movement potential. If properly design, this together with the self-weight and supplementary support from walls, buttresses and other parts of structure is sufficient to resist gravity and lateral forces.
Therefore carpentry joints are commonly used during wooden tiny house construction, for example when joining roof rafters, wall beams etc. The two by four structural system provides an advantage of using double slim profiles, which can be shifted to create overlaps or gaps in order to be easily connected to each other by cladding or over-cladding and thus using the carpentry joints methods. Mechanical metal fasteners, usually screws or nails, are used to secure the joint. Glue can be used to help strengthen the carpentry joints as well, however it is important to proceed carefully. It is recommended to have the fibres in contact areas be ideally perpendicular to each other, the least desirable is a version where they become sort of “extension”.
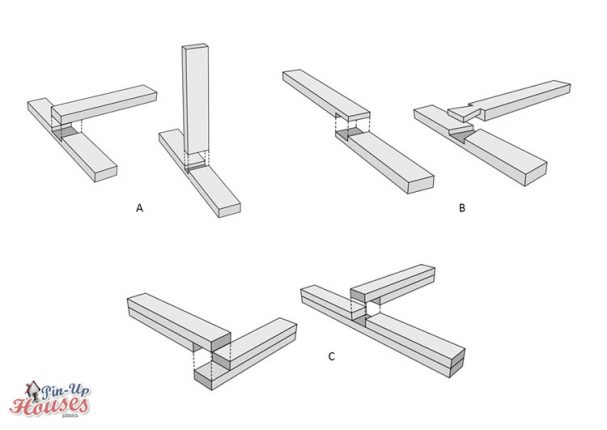
- A. Through dado joint
- B. Halving and dovetail halving joint
- C. Corner halving joint
Another advantage compared to the mechanical framing connectors is that they are made of wood just same as the rest of your DIY tiny house or small cabin, because in case of exposure to moisture their reaction and volume changes are similar to those of the entire structure. However they must be crafted properly and precisely, so a professional carpenter is often required.
Types of carpentry joints
Various types of carpentry joints are categorized according to their shape. Butt joint is the most basic type of joint, where one timber member is placed with its end against another one at right angle and attached with mechanical metal fasteners, usually screws or nails. Similar to that is a mitered butt joint, except in this case end of the member is mitered at 45° angle. It can be either on both members creating a neat corner or only one member with angle board clinging to a straight board. Halving joint, also known as half-lap joint, is suitable types of joints for moments when you need to join two pieces of wood at their middle part rather than at the ends. At the point of connection, same amount of wood is removed on both of the members to create a notch, which will allow them to flash together like pieces of puzzles. This type of joint is stronger than the butt joint and you can also strengthen it further more by using a glue.
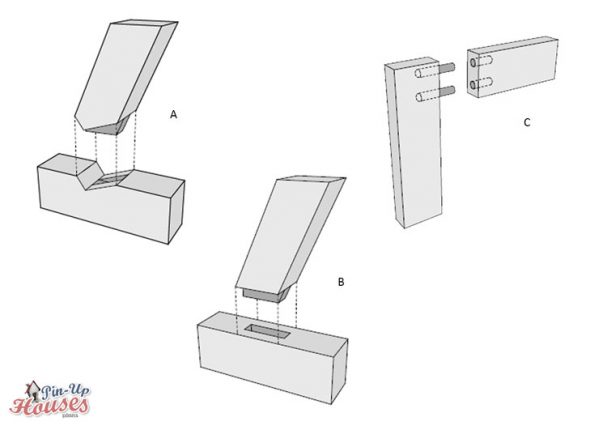
- A. Skewed mortise and tenon joint
- B. Skewed mortise and tenon joint
- C. Glued dowelled joint
Mortise and tenon joint is one of the oldest and classical of the woodworking joints. Mortise is created on side of one of the members and tenon of exactly same dimensions is protruding from the other member, which is then fitted into the first one. This connection is quite strong, especially when the pieces are at the right angle to each other, simple and has undeniable visual qualities. Tongue and groove joint is used for boards, very common for example in wooden floors, and works similarly with the method of one member fitting inside the other one. It connects two boards being placed next to each other: one has a groove notched out all along its side edge and the other has a tongue fitting exactly into the groove, so that the two boards can hold together tightly.
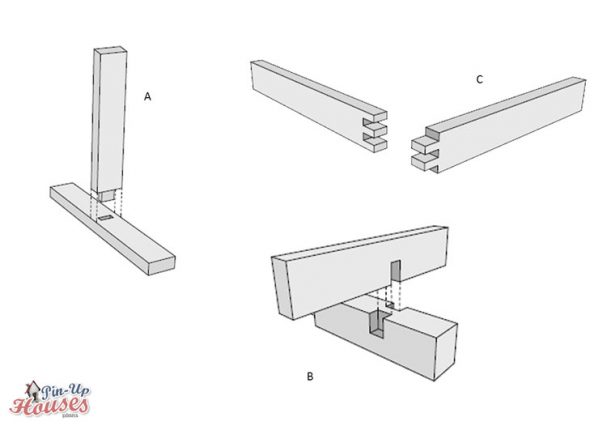
- A. Mortise and tenon joint
- B. T-bridle / halving joint
- C. Dovetail joint
Dovetail joint is probably one of the most visually pleasing one from the types of carpentry joints. It can be used for two members attached to each other at their ends at right angle. On each end notches are created in such a way, that they can fit precisely and very tightly together, so this joint is usually very strong and does not come loose. Dado joint is another of the joints, which works with fitting the two members together, but in this case only one of them is adjusted. A square notch is cut in center of one of the members so that the other one, positioned at right angle, can fit into it. There is also a version where dado is cut at the end of the member instead of the middle and in such case it is called rabbet joint.
How to build a tiny house construction guide
Would you like to learn more about small timber structure, DIY house plans, timber framing connectors, mechanical metal fasteners and other issues related to easy to build small houses? Well we have a book for you! This step by step guide How to build a tiny house will lead you through every part of timber construction, available to order in electronic or printed version here.









